10 KiB
| title | head_inline |
|---|---|
| Dockerized VoLTE Setup | <style> .blue { color: blue; } </style> |
Setup description:
- MCC: 001, MNC: 01
- Docker-compose
- srsENB + USRP B210 or a commercial eNB
- Sysmocom USIM - sysmoUSIM-SJS1
- UE: Mi 9 Pro 5G. Other UE are being tested. {: .blue}
0. Introduction
This tutorial introduces an install-and-run lab for Open5GS + Kamailio IMS VoLTE study, a follow-up project of Open5GS Tutorial: VoLTE Setup with Kamailio IMS and Open5GS. The tutorial is based on Herle Supreeth's docker_open5gs and his fork of Open5GS and Kamailio.
The main purpose is to save researchers' and students' time to debug for a minimum-viable environment before actual study can be proceeded.
Important notice before you start
- Herle Supreeth's fork of Kamailio is used to support IPsec.
- Java 7 is downloaded from an alternative location. You have to agree with Oracle's term of service and have an Oracle account, to legally use Java SDK 7u80. By using this repo, I assume you have the legal right to use it and hold no liability.
You have to prepare IMSI, Ki, OP (yes, not OPc), SQN of your SIM cards. Even though Open5GS supports OPc, FHoSS merely takes OP. You may also want to disable SQN checking in the SIM card (even though we are not sure whether it is effective.) Check out https://github.com/herlesupreeth/sysmo-usim-tool for a slightly modified sysmo-usim-tool.
1. Prepare SIM cards for VoLTE
N.B.
- Wrong KIC / KID / KIK bricks your SIM card.
- Use MCC = 001, MNC = 01 for a testing network, unless you know your MCC/MNC is supported by Android Carrier Privileges.
Refer to: https://osmocom.org/projects/cellular-infrastructure/wiki/VoLTE_IMS_Android_Carrier_Privileges
- gp --key-enc KIC1 --key-mac KID1 --key-dek KIK1 -lvi
- gp --key-enc KIC1 --key-mac KID1 --key-dek KIK1 --unlock
- gp --install applet.cap
- gp -a 00A4040009A00000015141434C0000 -a 80E2900033F031E22FE11E4F06FFFFFFFFFFFFC114E46872F28B350B7E1F140DE535C2A8D5804F0BE3E30DD00101DB080000000000000001
- gp --acr-list
If you use gp.jar from Herle Supreeth's CoSIM Wiki, replace gp --acr-list with gp --acr-list-aram.
2. Build Open5GS, Kamailio with docker-compose
Mandatory requirements:
Install docker-compose and make sure it works before going forward.
Clone the repository and build base docker images of open5gs and Kamailio:
git clone https://github.com/miaoski/docker_open5gs
cd docker_open5gs/base
docker build --no-cache --force-rm -t docker_open5gs .
cd ../kamailio_base
docker build --no-cache --force-rm -t open5gs_kamailio .
cd ..
docker-compose build --no-cache
# Copy DNS setting to containers. Do this whenever you change IP in .env
./copy-env.sh
# Start MySQL and MongoDB first, in order to initialize the databases
docker-compose up mongo mysql dns
# To start Open5GS core network without IMS
docker-compose up hss mme pcrf pgw sgw
# To start IMS
docker-compose up rtpengine fhoss pcscf icscf scscf
# To test whether DNS is properly running
./test-dns.sh
You may want to review .env for IP allocation.
3. (Optional) Run srsENB in a separate container
I use srsENB and USRP B210 in the lab. Sometimes you may want to restart srsENB while keeping the core network running. It is thus recommended to run srsENB separately.
Edit .env first to set EARFCN, TX_GAIN, RX_GAIN. Thereafter,
docker-compose -f srsenb.yaml build --no-cache
docker-compose -f srsenb.yaml up
4. Configuration and register two UE
The configuration files for each of the Core Network component can be found
under their respective folder. Edit the .yaml files of the components and run
docker-compose build again.
Open (http://<DOCKER_HOST_IP>:3000) in a web browser, where <DOCKER_HOST_IP> is the IP of the machine/VM running the open5gs containers. Login with following credentials
Username : admin
Password : 1423
Follow the instructions in VoLTE Setup:
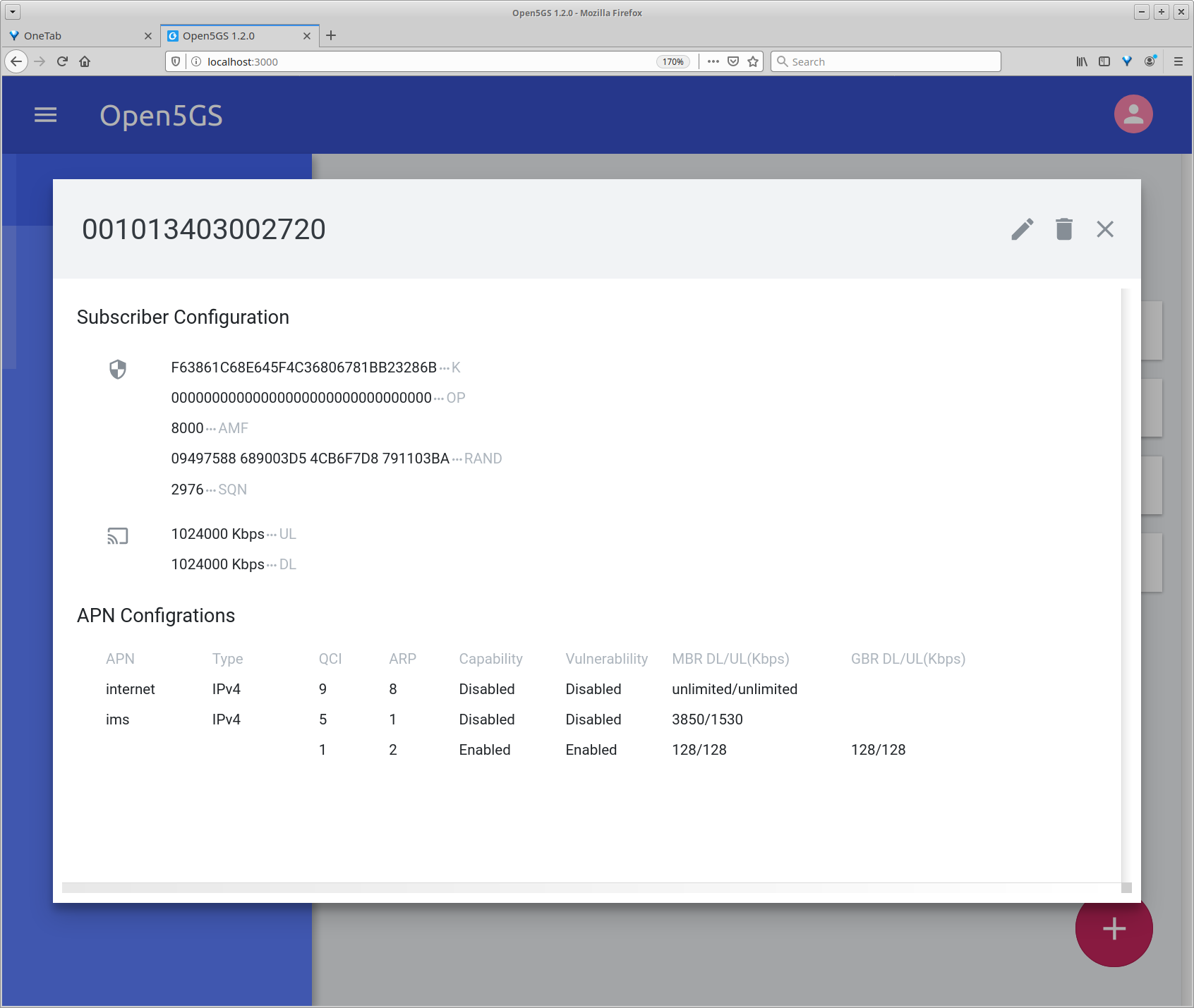
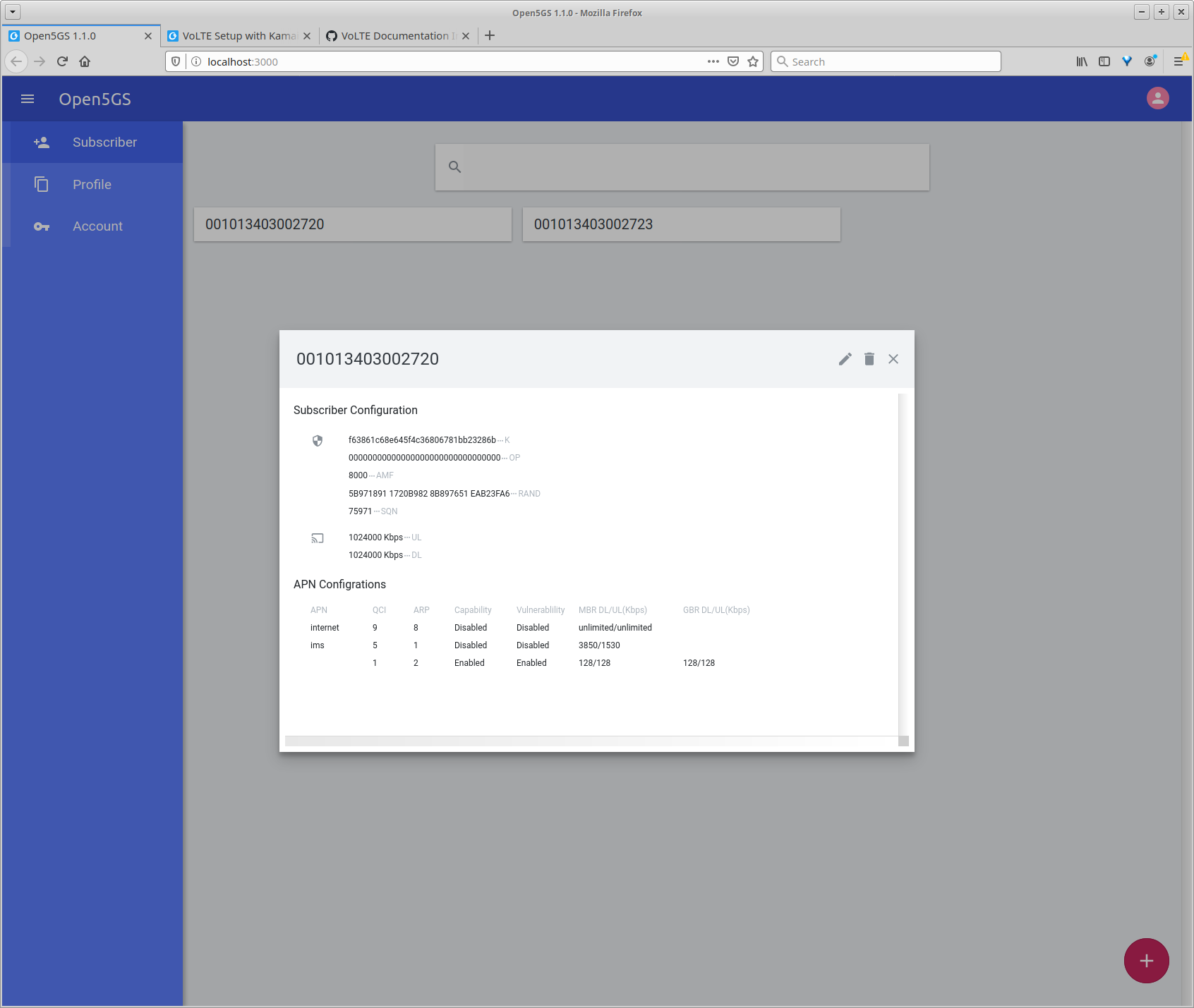
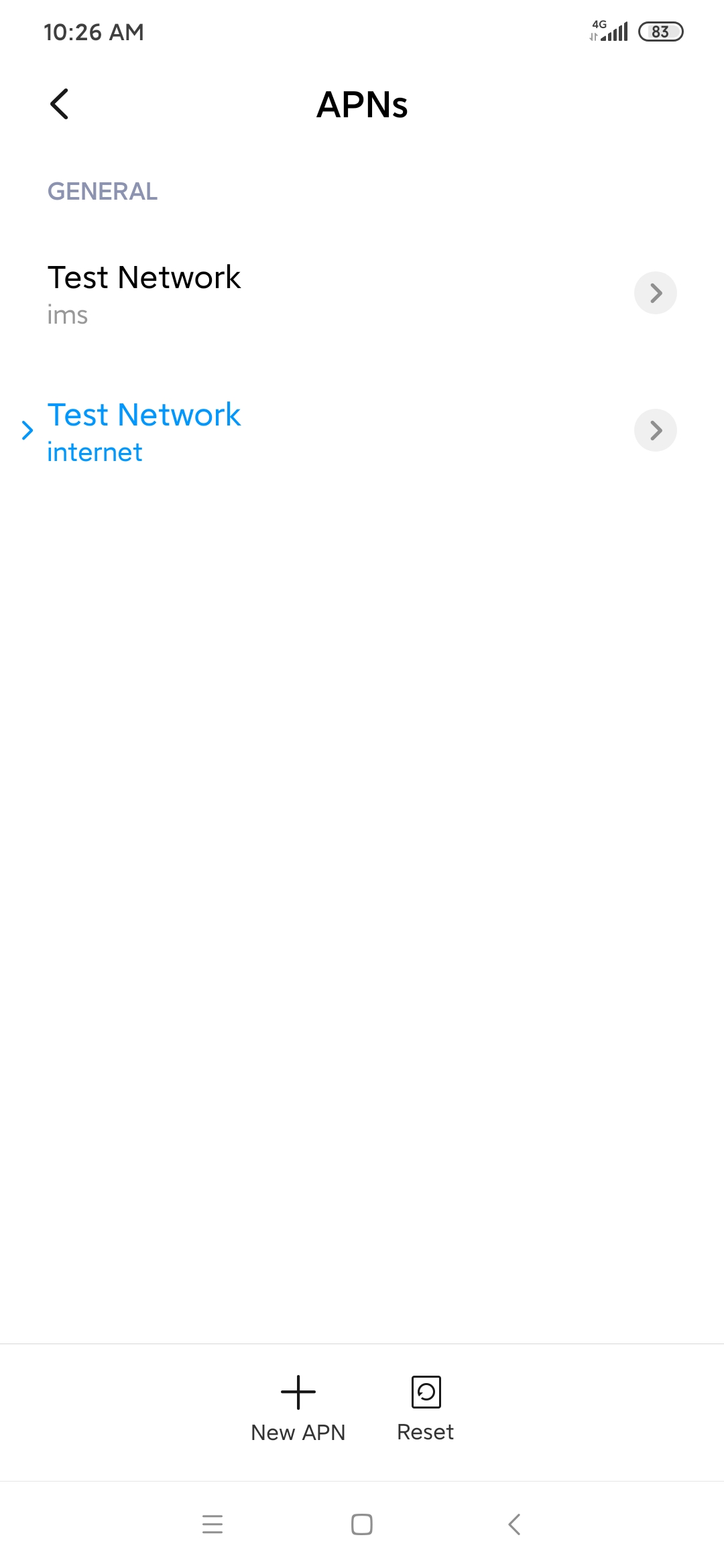
- Step 18, set IMSI, Ki, OP, SQN and APN of your SIM cards. <<<<<<< HEAD
- Step 20, add IMS subscriptions to FHoSS.
======= Important! Set the type of both APN to IPv4. Kamailio does not support VoLTE over IPv6 at the moment. (See the screenshot below.)
- Step 20, add IMS subscriptions to FHoSS.
master For already running systems, copy SQN from Open5GS and type it in FHoSS. You can type SQN in decimal. FHoSS will automagically convert it to hex.
Pay special attention to copy/paste. You might have leading or trailing spaces in FHoSS, resulting in failed connections!
<<<<<<< HEAD
master
5. Debugging with Wireshark
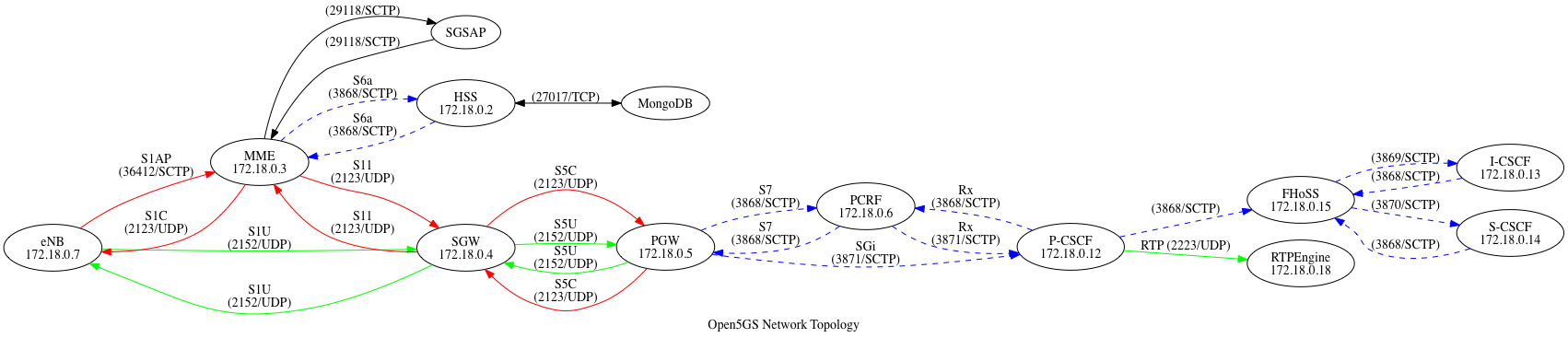
Thanks to Open5GS, the topology is super similar to SAE on Wikipedia.
APN
<<<<<<< HEAD APN Configurations in Open5GS should look like this one.
=======
master On your cellphone, there should be internet and ims.
CoIMS should look like the one below. If you don't know what CoIMS is, please refer to step 23 of VoLTE Setup.

Networking issues
PCAP files of successful calls can be found on VoLTE Setup.
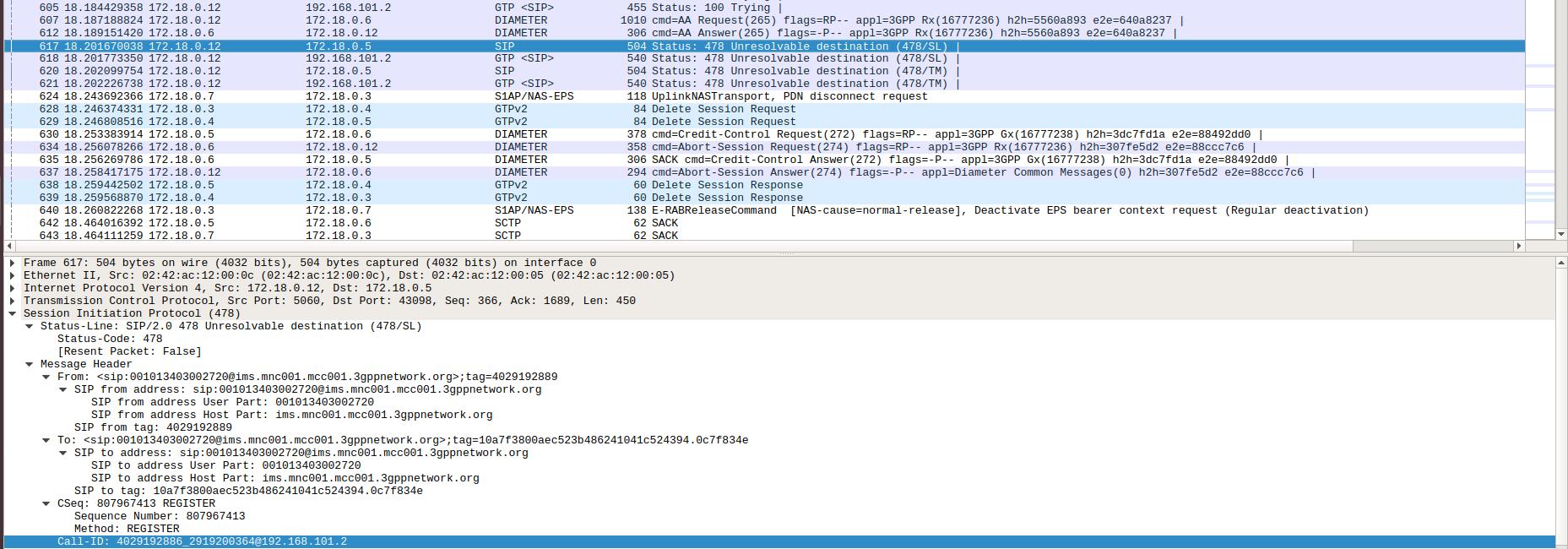
When DNS is not properly set, you may end up with 478 Unresolvable destination (478/SL):
If the port if not open, or DNS is not properly configured, the phone cannot reach P-CSCF and fails.
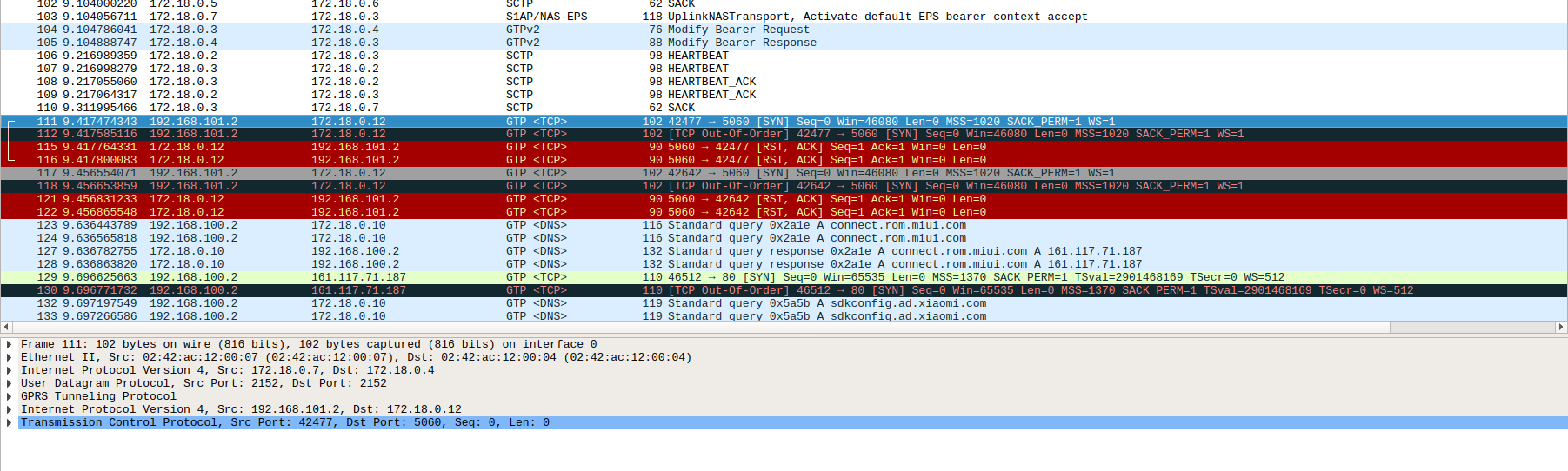
If your cellphone stuck on ipsec (like mine), the PCAP looks like the one below. However, it means almost every function in the system works (only RTPEngine and FHoSS are not tested.)
6. Successful calls
Herle Supreeth has shared PCAP files of successful calls, including
- [IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to Non-IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_nonipsec_call.pcapng)
The successful calls were made with a commercial eNB (in his case a Casa smallcell), while srsENB the ACK takes a very long time to reach the UE, resulting in disconnected calls.
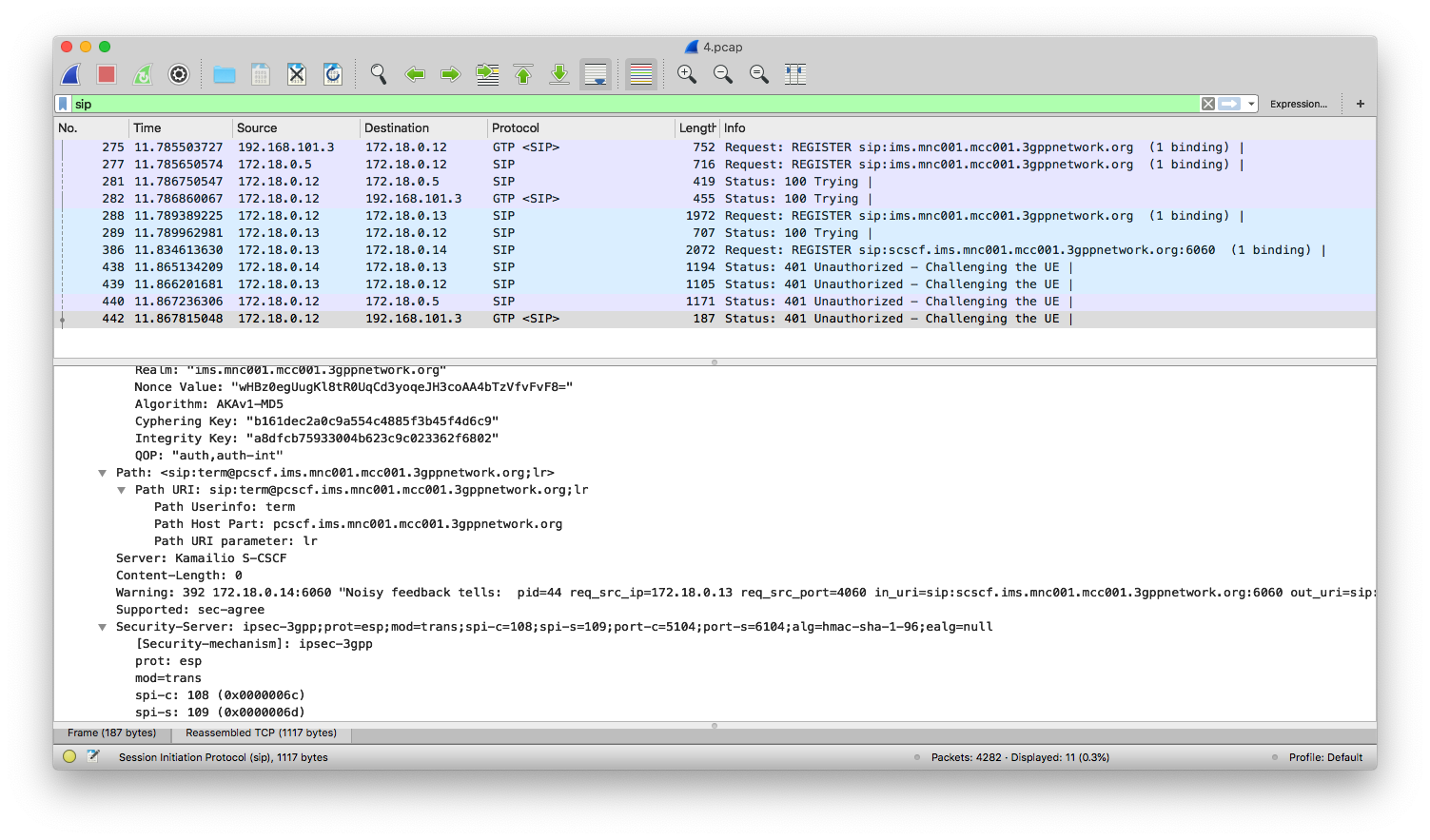
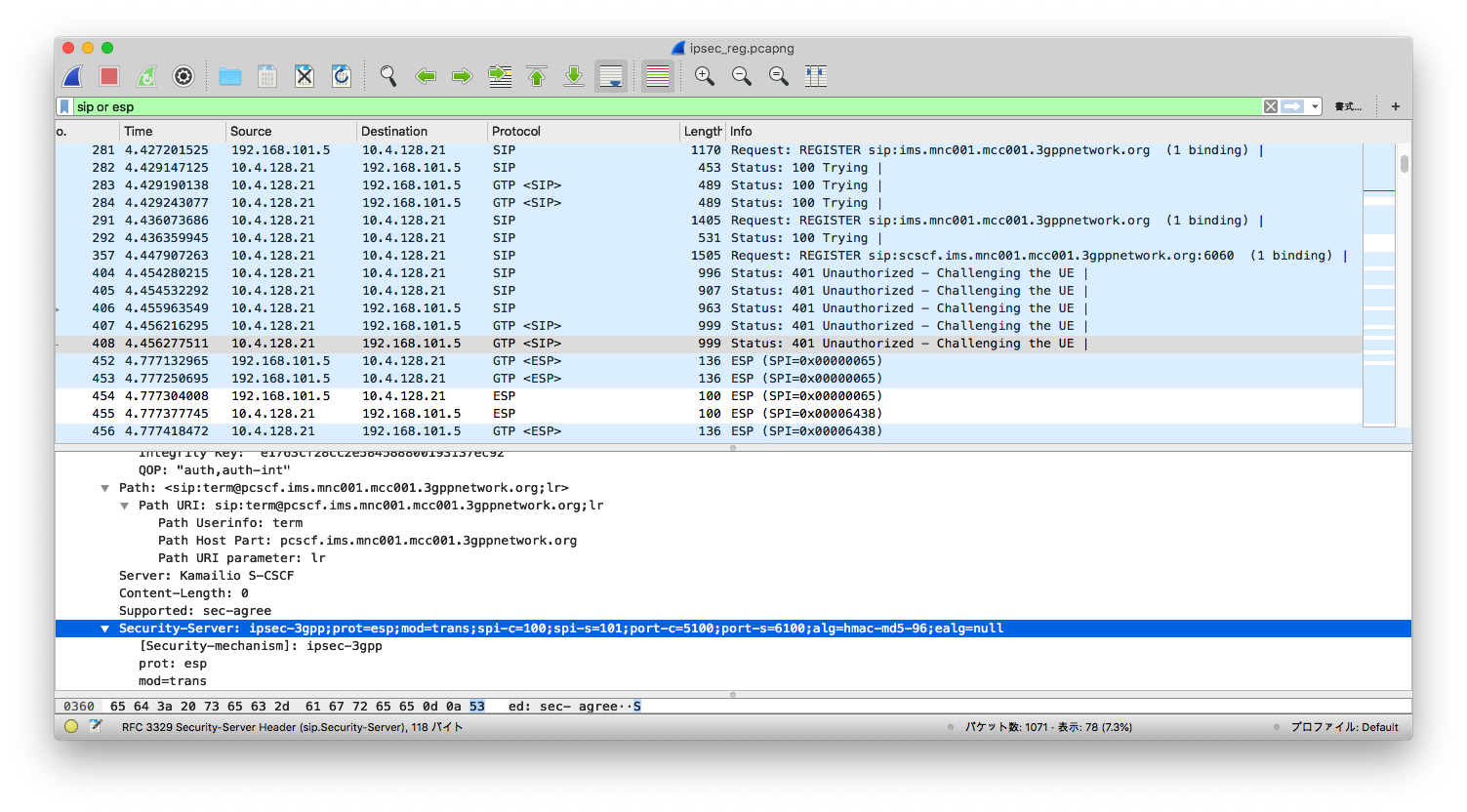
UE registration
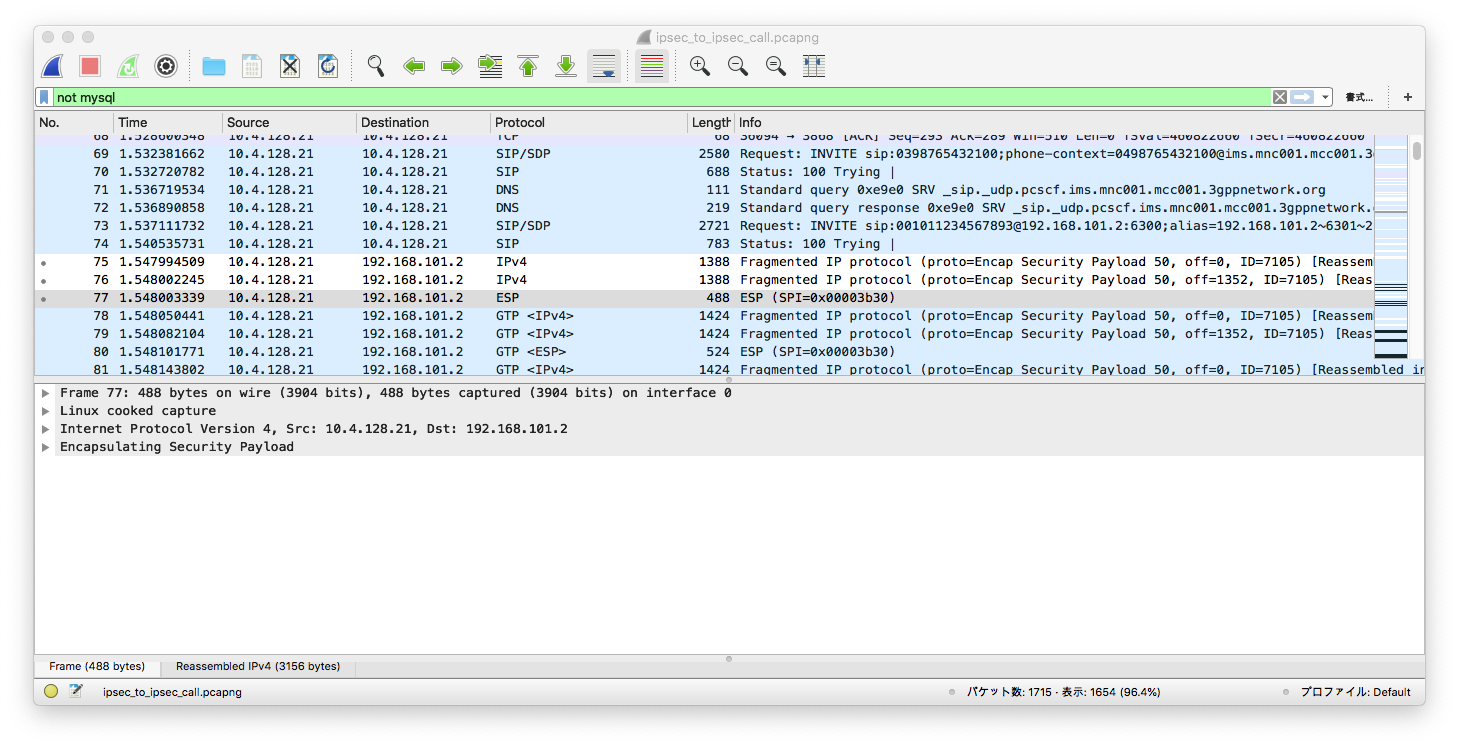
From the screenshot, we see a UE that supports IPSec got a response from S-CSCF, indicating that ipsec-3gpp is supported, protocol is ESP (ethernet proto 50, IPSec). Client port (port-c) is 5100 and server port (port-s) 6100. Refer to IMS/SIP - Basic Procedures if you want to know more. Also, notice that packets after 401 Unauthorized are transmitted over ESP.
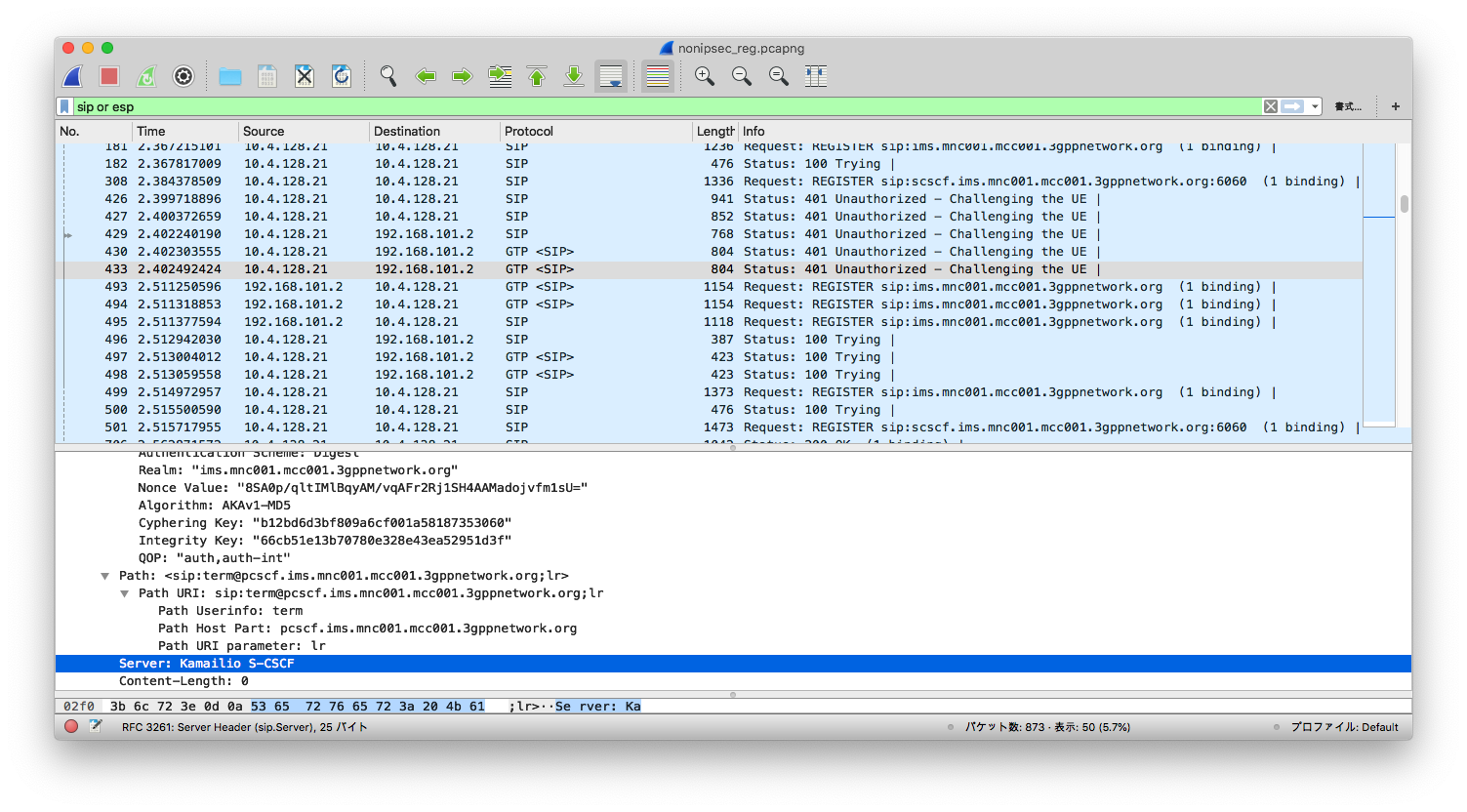
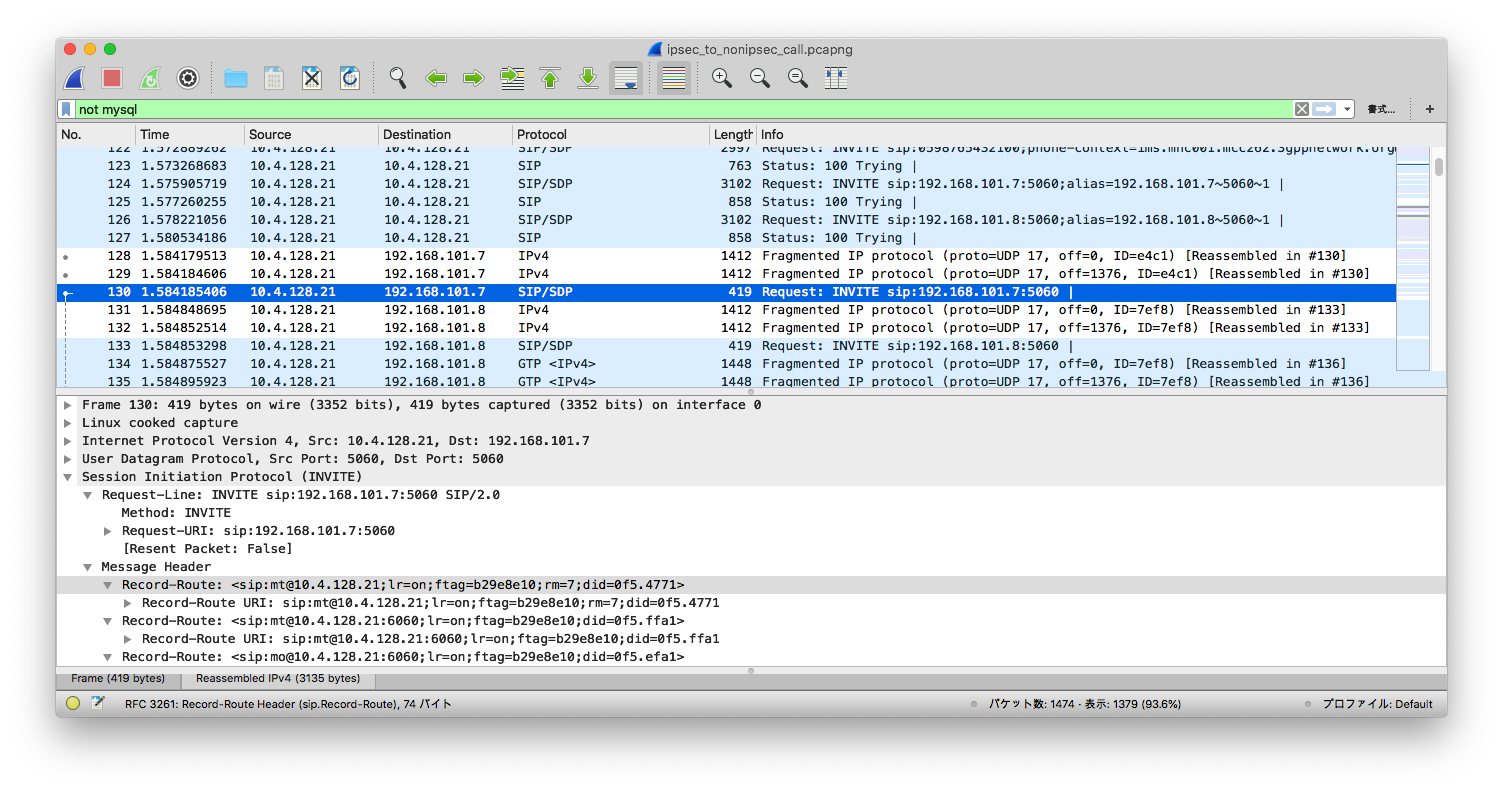
If a UE does not support IPSec, you don't see the "security-server", as shown below:
VoLTE calls
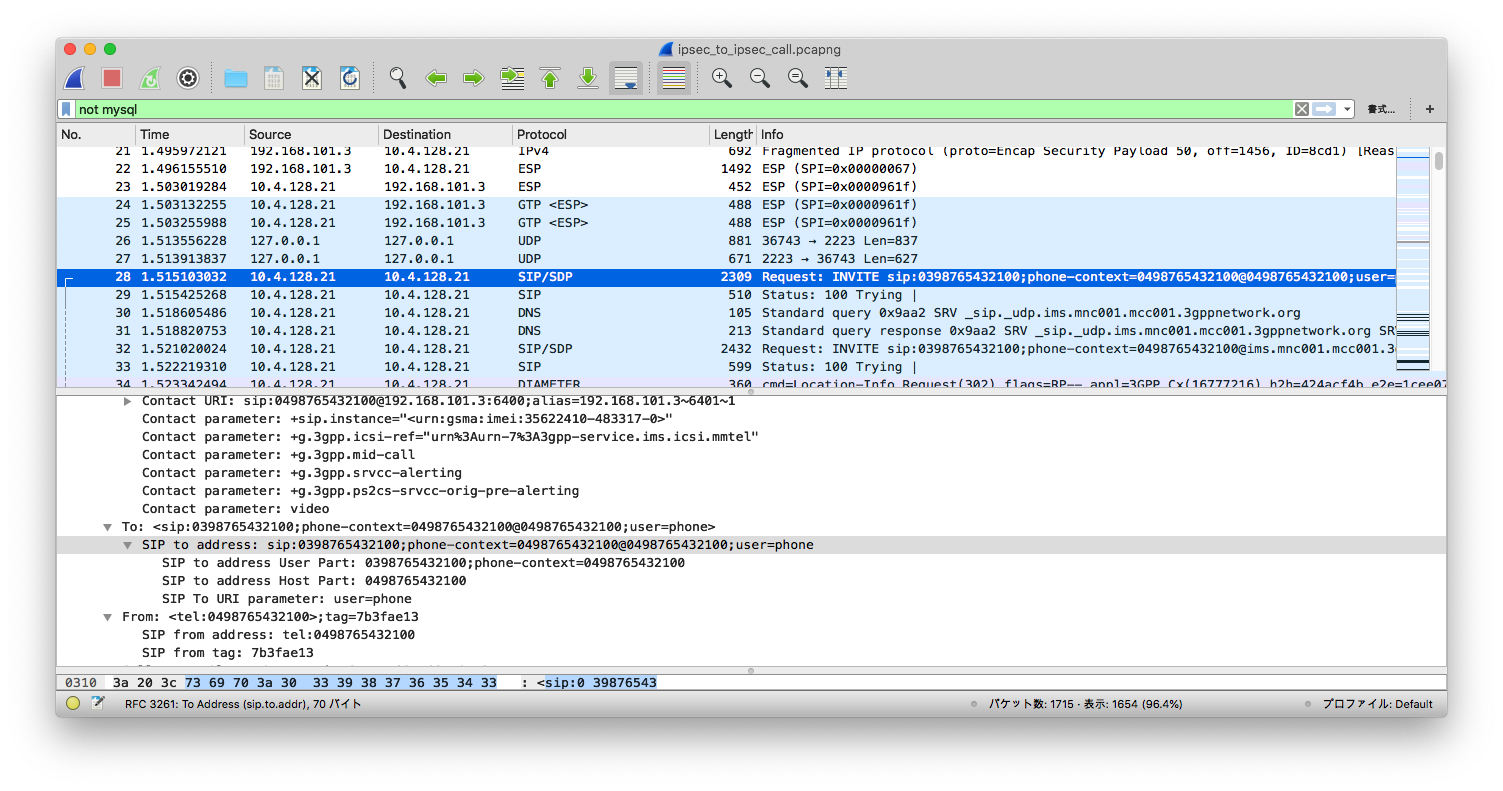
The Wireshark above shows that after several IPSec (ESP) packets, S-CSCF is sending a SIP INVITE for UE 03 to UE 04. To be more precise,
Request-Line: INVITE sip:0398765432100;phone-context=0498765432100@0498765432100;user=phone SIP/2.0
...
Record-Route URI: sip:mo@10.4.128.21:6101;lr=on;ftag=7b3fae13;rm=8;did=078.654
The SIP port of the caller (contact) will also be passed to the callee,
Contact URI: sip:0498765432100@192.168.101.3:6400;alias=192.168.101.3~6401~1
After S-CSCF forwarded the INVITE to P-CSCF, it returns a 100 Trying, and contacts with the callee via IPSec:
This can be contrasted when the callee does not support IPSec. After 100 Trying, a UE that does not support IPSec is sent a SIP INVITE in clear text:
7. Known issues
- IPv6 is not supported.
- If your cellphone mandates IPsec (such as Xiaomi Mi 9 Pro 5G), it might not work. However, you should at least see SIP REGISTRATION and a couple of 401 Unauthorized.
If anyone successfully made a VoLTE call by using this repo, please submit an issue and let me know!