is the IP of the machine/VM running the open5gs containers. Login with following credentials
```
Username : admin
Password : 1423
```
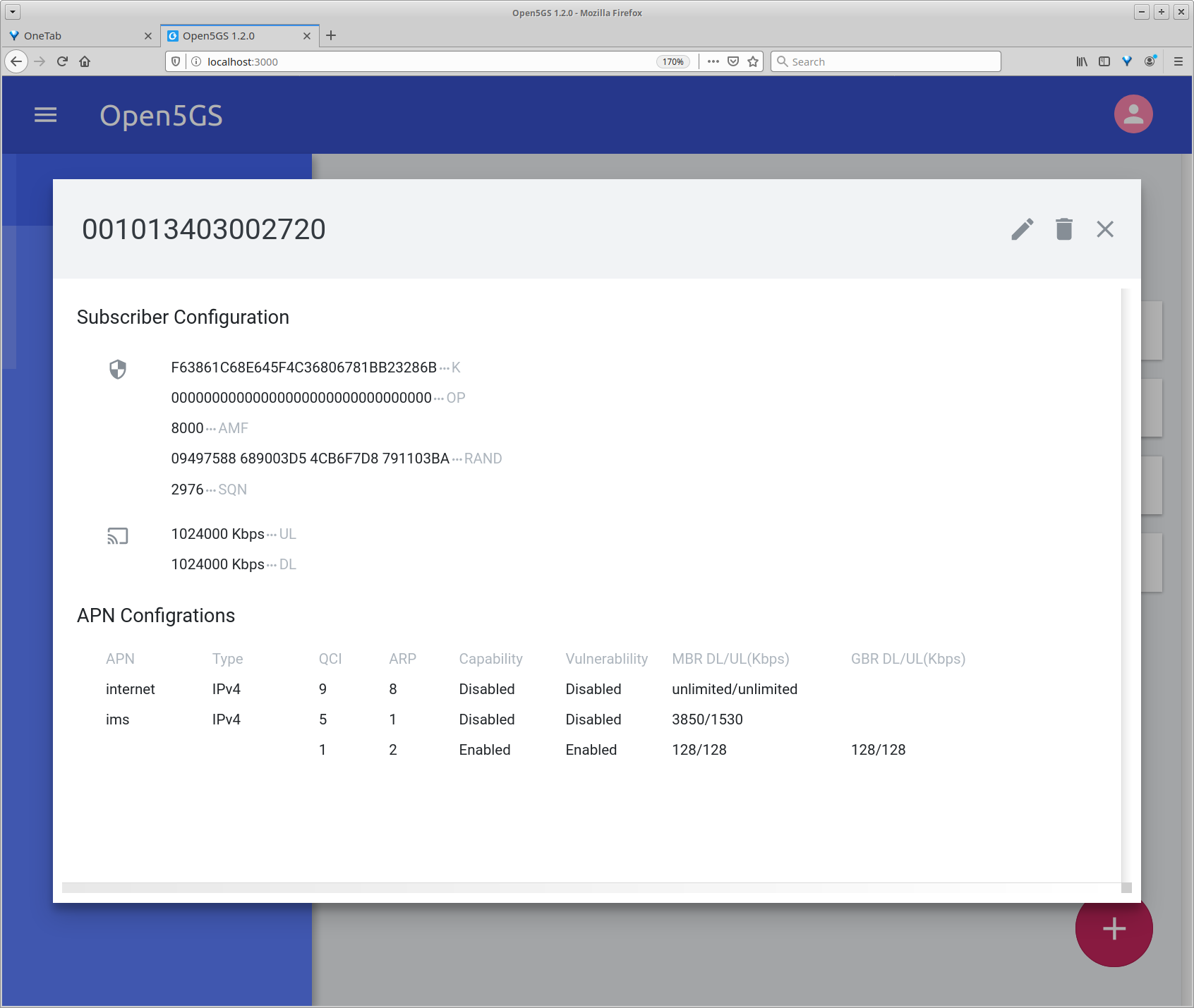
Add users with their corresponding IMSI, Ki, OP/OPc value and APN settings. The APN settings should look like below:
APN Configuration:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| APN | Type | QCI | ARP | Capability | Vulnerablility | MBR DL/UL(Kbps) | GBR DL/UL(Kbps) | PGW IP |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| internet | IPv4 | 9 | 8 | Disabled | Disabled | unlimited/unlimited | | |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
| ims | IPv4 | 5 | 1 | Disabled | Disabled | 3850/1530 | | |
| | | 1 | 2 | Enabled | Enabled | 128/128 | 128/128 | |
| | | 2 | 4 | Enabled | Enabled | 128/128 | 128/128 | |
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
**Important!** Set the type of both APN to IPv4. Kamailio does not support VoLTE over IPv6 at the moment. (See the screenshot below)
- Provision IMSI and MSISDN in osmohlr to allow [SMS over SGs](https://github.com/herlesupreeth/docker_open5gs#provisioning-of-imsi-and-msisdn-with-osmohlr-as-follows)
- Provision SIM information in pyHSS [IMS](https://github.com/herlesupreeth/docker_open5gs#provisioning-of-sim-information-in-pyhss-is-as-follows)
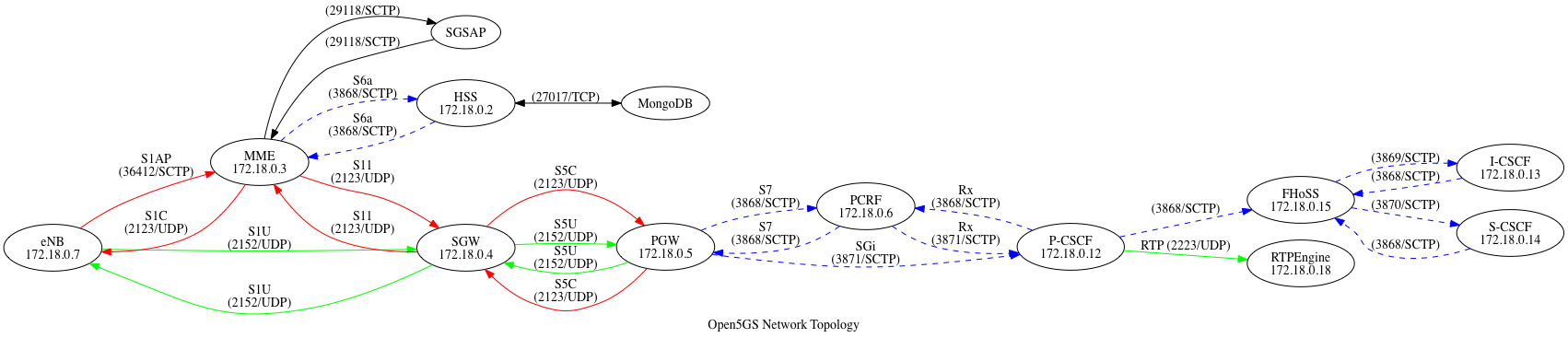
#### 7. Debugging with Wireshark
Thanks to Open5GS, the topology is super similar to [SAE on Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/System_Architecture_Evolution#/media/File:Evolved_Packet_Core.svg).
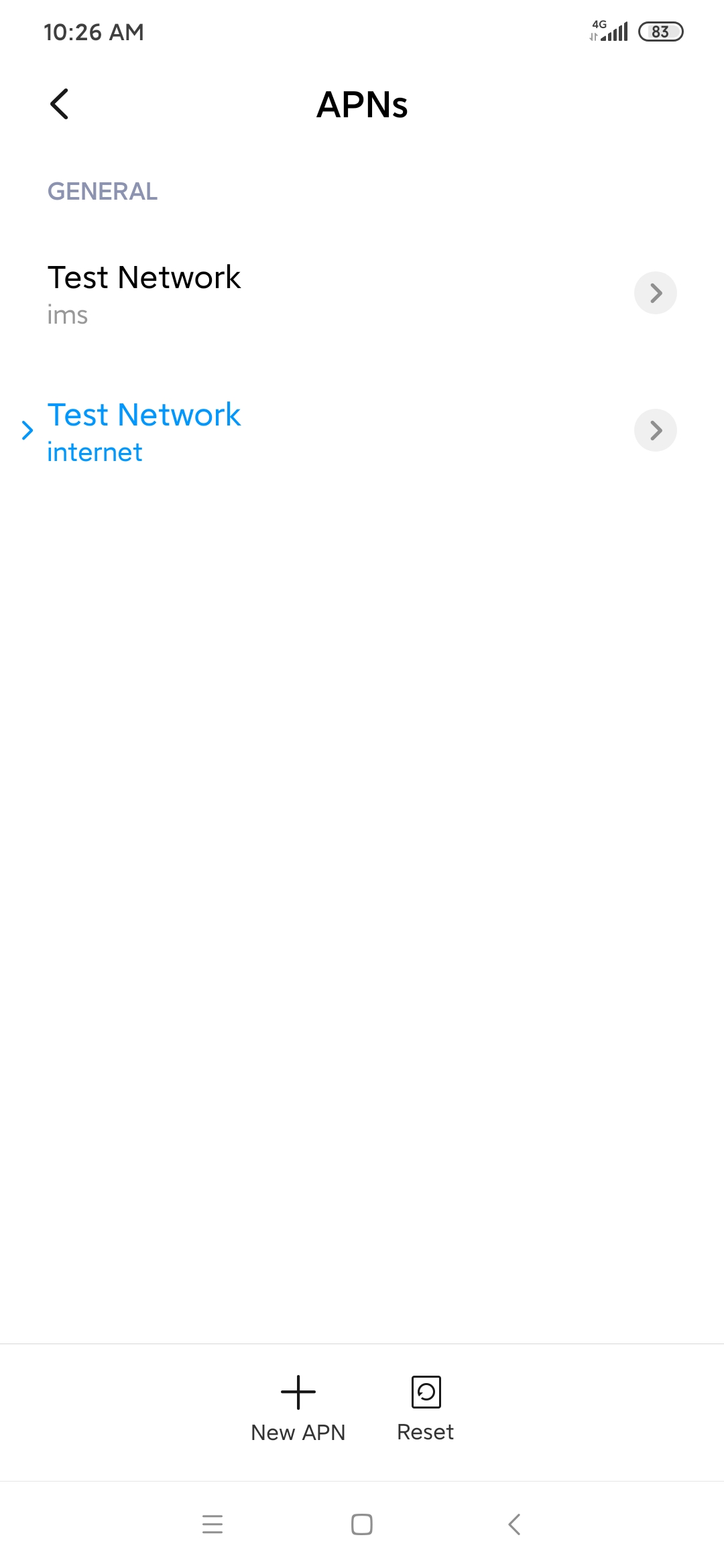
**APN**
On your cellphone, there should be *internet* and *ims*.
 If CoIMS is used to force enable VoLTE on the Android device, it should look like in the screenshot below:
If CoIMS is used to force enable VoLTE on the Android device, it should look like in the screenshot below:
 **Networking issues**
PCAP files of successful calls can be found on [VoLTE Setup](https://open5gs.org/open5gs/docs/tutorial/02-VoLTE-setup/).
When DNS is not properly set, you may end up with 478 Unresolvable destination (478/SL):
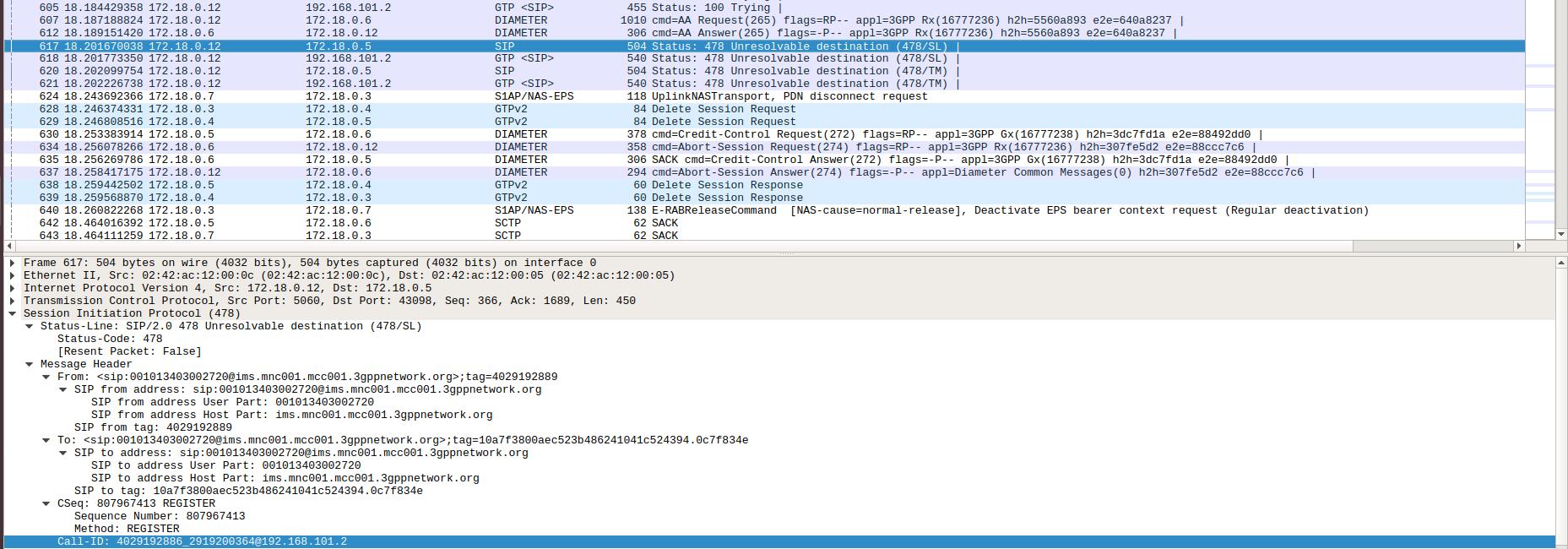
If the port if not open, or DNS is not properly configured, the phone cannot reach P-CSCF and fails.
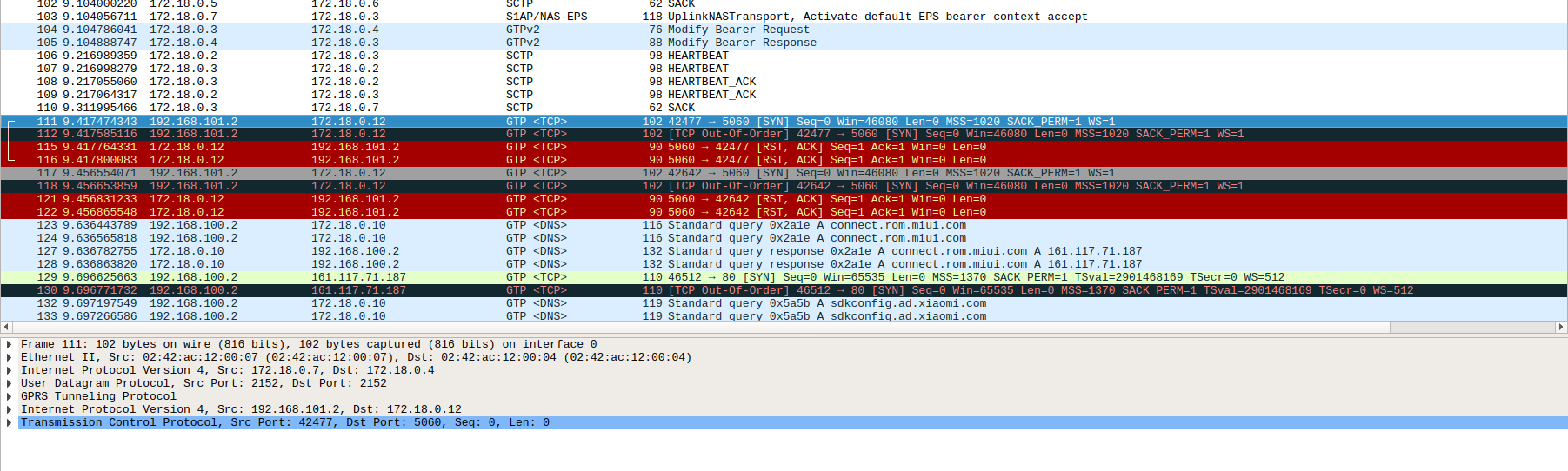
If there is an NAT between PGW and P-CSCF, IPsec-NAT would not work, and the PCAP looks like the one below. Note that you need to run P-CSCF as root, in
order to add xfrm state and policy.
#### 8. Successful calls
Herle Supreeth has shared PCAP files of successful calls, including
- [IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to Non-IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_nonipsec_call.pcapng)
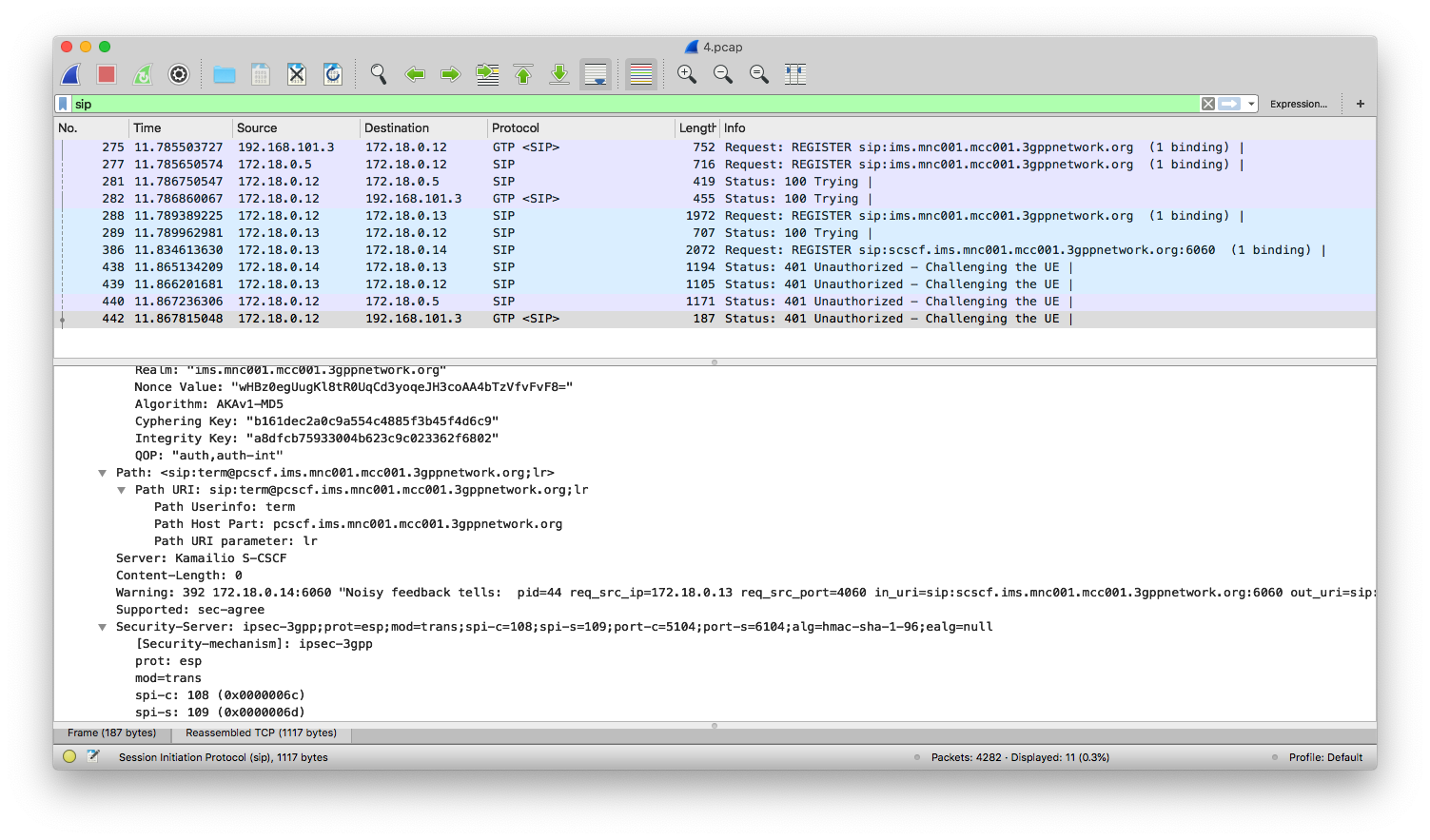
**UE registration**
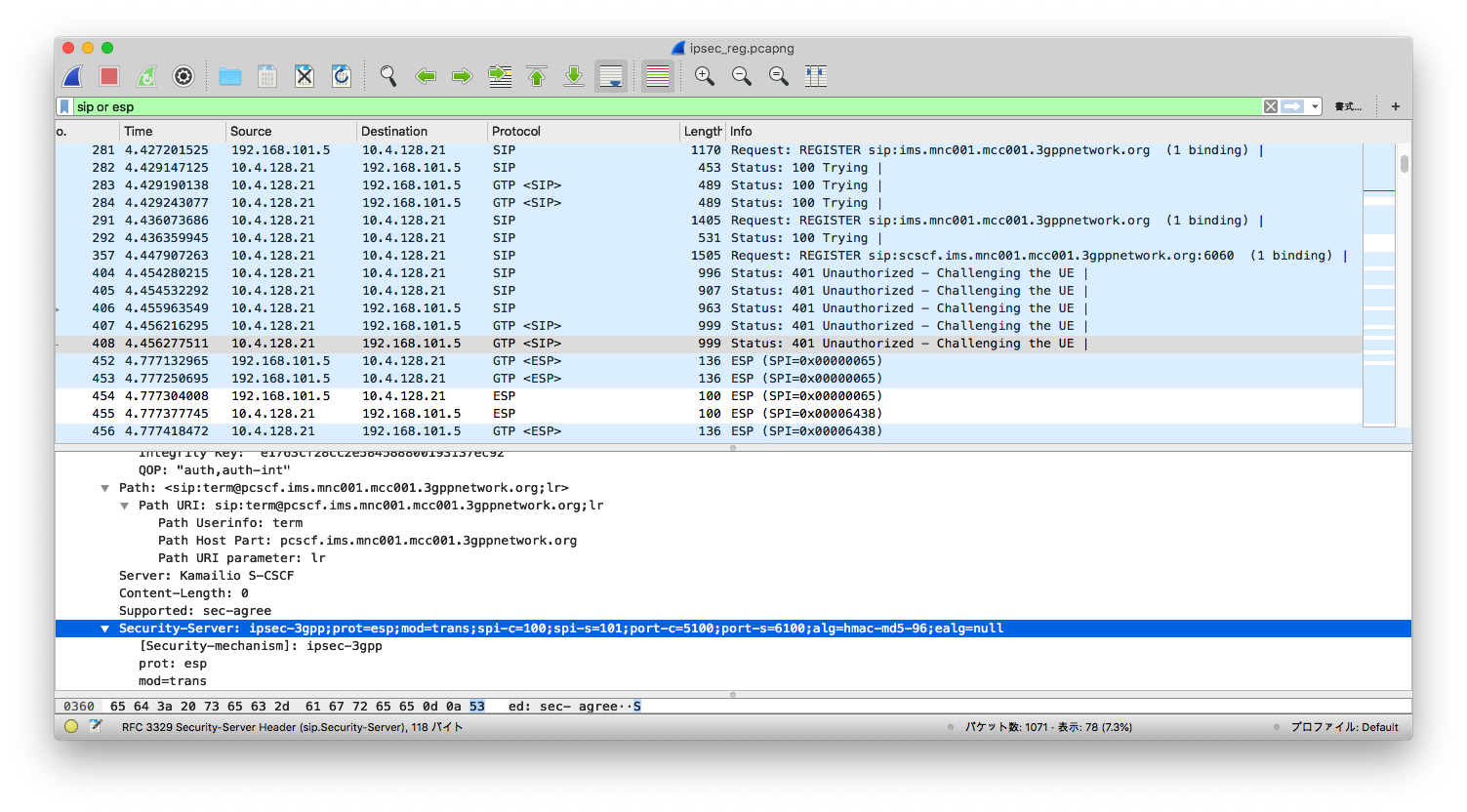
From the screenshot, we see a UE that supports IPSec got a response from S-CSCF, indicating that ipsec-3gpp is supported, protocol is ESP (ethernet proto 50, IPSec). Client port (port-c) is 5100 and server port (port-s) 6100.
Refer to [IMS/SIP - Basic Procedures](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/IMS_SIP_Procedure_Reg_Auth_IPSec.html) if you want to know more.
Also, notice that packets after 401 Unauthorized are transmitted over ESP.
If a UE does not support IPSec, you don't see the "security-server", as shown below:
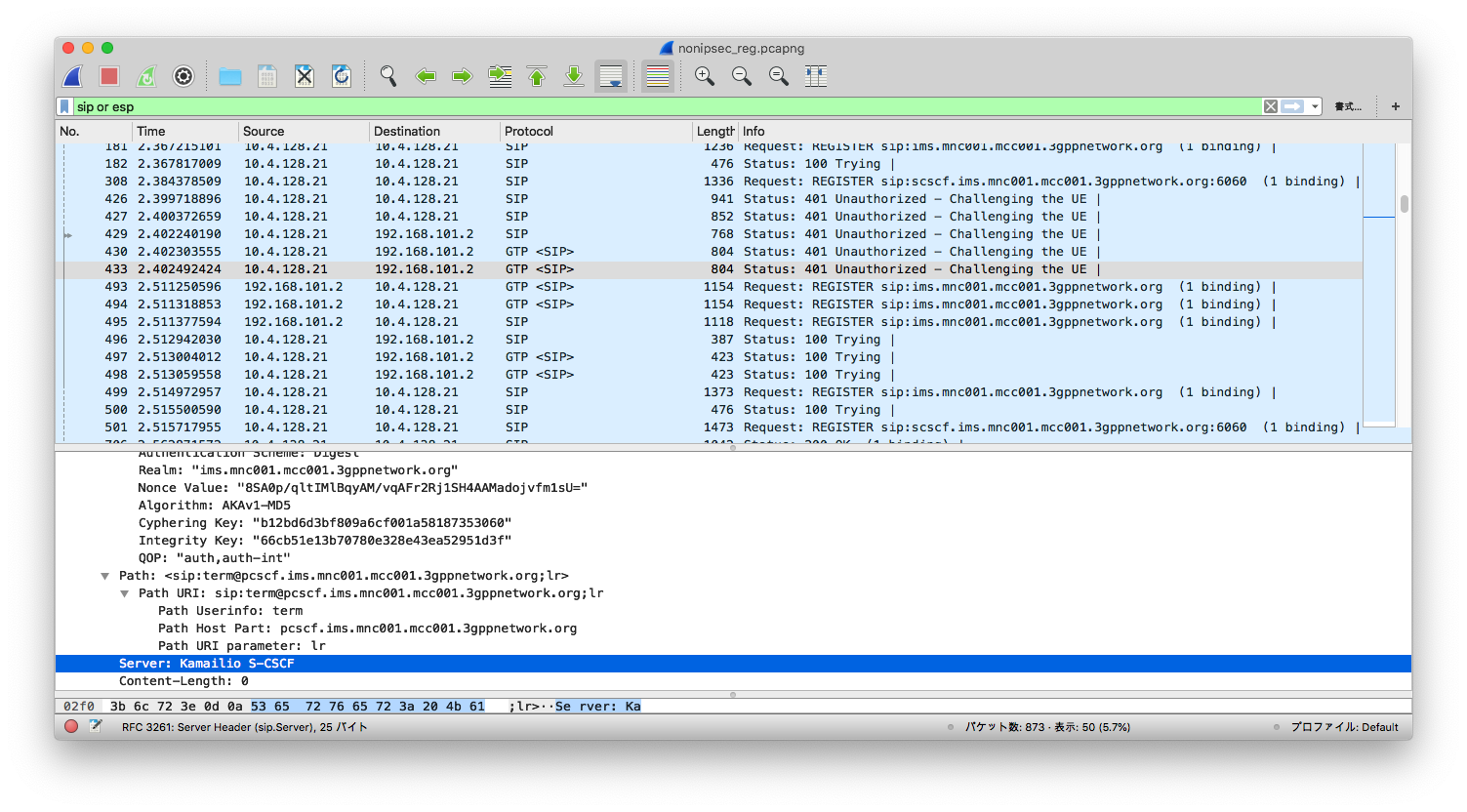
**VoLTE calls**
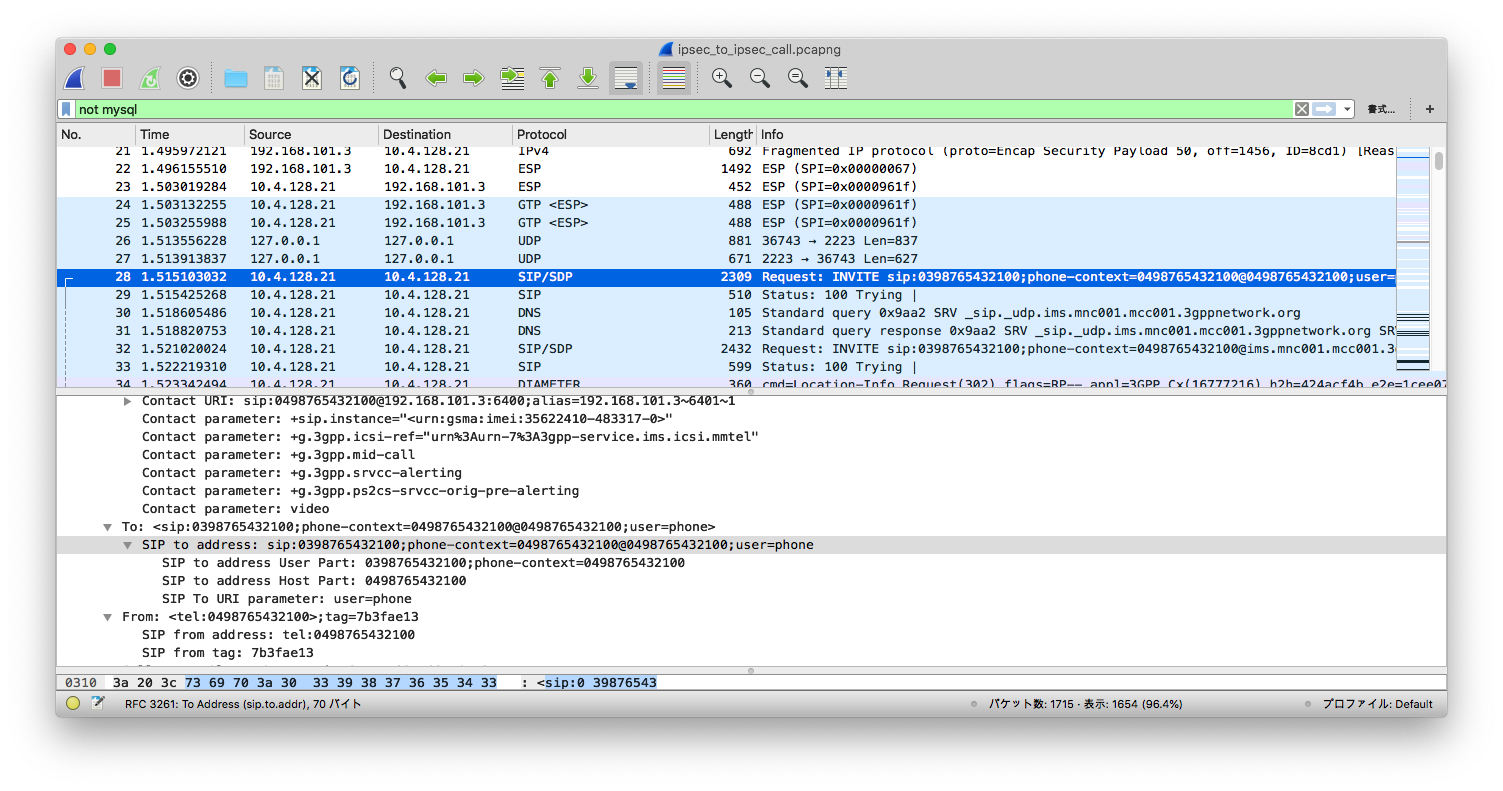
The Wireshark above shows that after several IPSec (ESP) packets, S-CSCF is sending a SIP INVITE for UE 03 to UE 04. To be more precise,
```
Request-Line: INVITE sip:0398765432100;phone-context=0498765432100@0498765432100;user=phone SIP/2.0
...
Record-Route URI: sip:mo@10.4.128.21:6101;lr=on;ftag=7b3fae13;rm=8;did=078.654
```
The SIP port of the caller (`contact`) will also be passed to the callee,
```
Contact URI: sip:0498765432100@192.168.101.3:6400;alias=192.168.101.3~6401~1
```
After S-CSCF forwarded the INVITE to P-CSCF, it returns a 100 Trying, and contacts with the callee via IPSec:
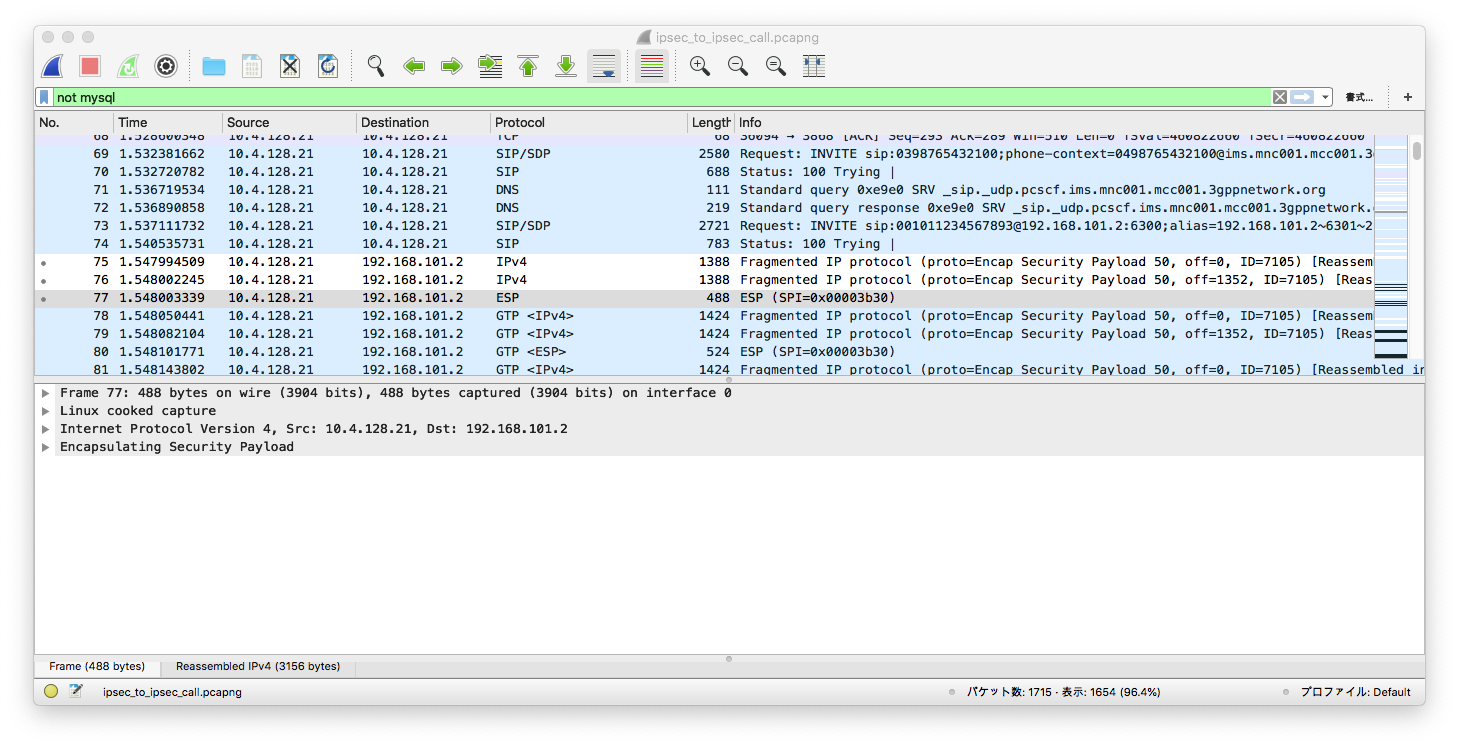
This can be contrasted when the callee does not support IPSec. After 100
Trying, a UE that does not support IPSec is sent a SIP INVITE in clear text:
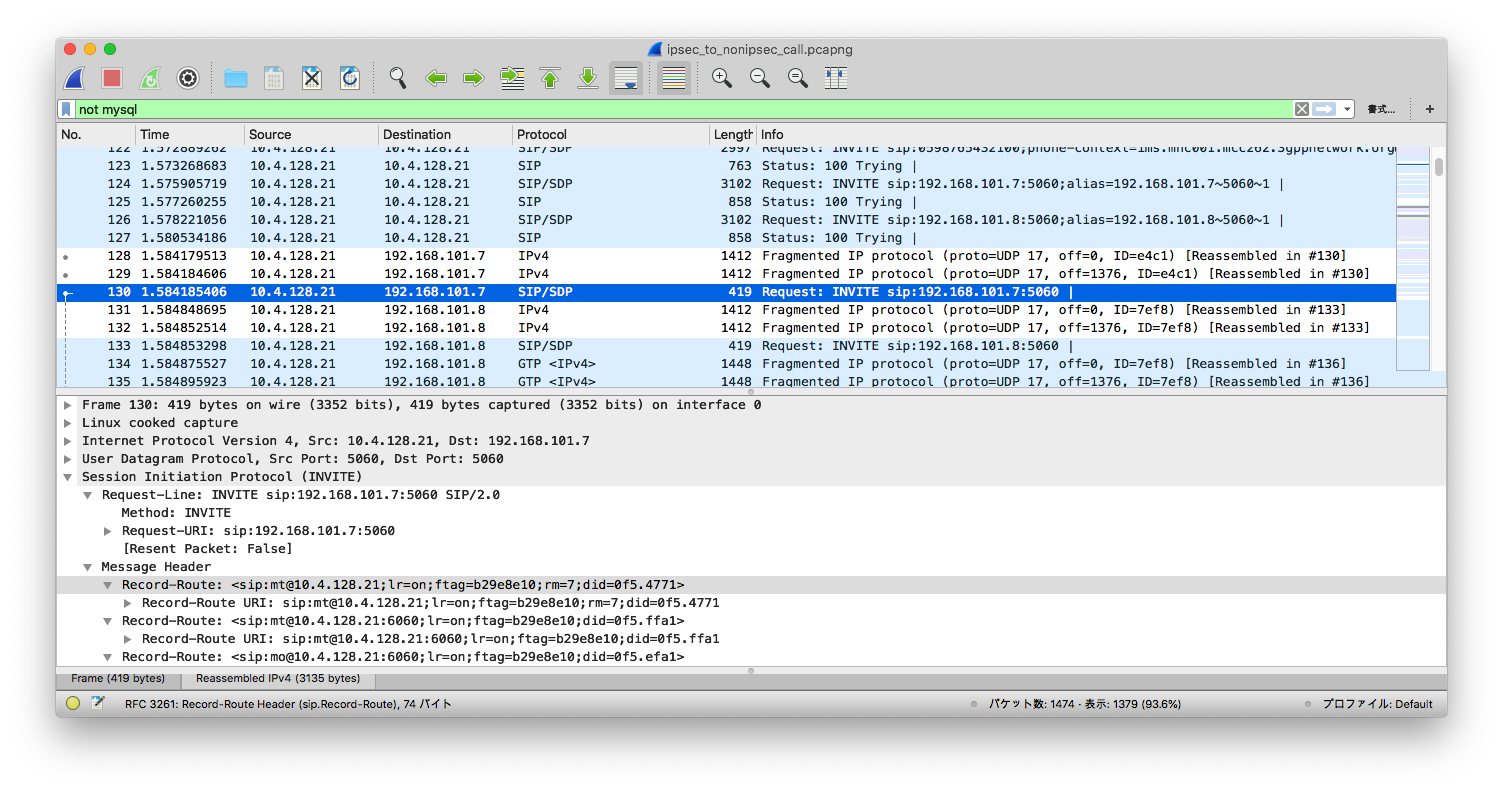
#### 9. Known issues
- IPv6 is not supported.
#### 10. References
- [https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284](https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284)
- [https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/](https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/)
- [https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html)
**Networking issues**
PCAP files of successful calls can be found on [VoLTE Setup](https://open5gs.org/open5gs/docs/tutorial/02-VoLTE-setup/).
When DNS is not properly set, you may end up with 478 Unresolvable destination (478/SL):

If the port if not open, or DNS is not properly configured, the phone cannot reach P-CSCF and fails.

If there is an NAT between PGW and P-CSCF, IPsec-NAT would not work, and the PCAP looks like the one below. Note that you need to run P-CSCF as root, in
order to add xfrm state and policy.

#### 8. Successful calls
Herle Supreeth has shared PCAP files of successful calls, including
- [IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to Non-IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_nonipsec_call.pcapng)
**UE registration**

From the screenshot, we see a UE that supports IPSec got a response from S-CSCF, indicating that ipsec-3gpp is supported, protocol is ESP (ethernet proto 50, IPSec). Client port (port-c) is 5100 and server port (port-s) 6100.
Refer to [IMS/SIP - Basic Procedures](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/IMS_SIP_Procedure_Reg_Auth_IPSec.html) if you want to know more.
Also, notice that packets after 401 Unauthorized are transmitted over ESP.
If a UE does not support IPSec, you don't see the "security-server", as shown below:

**VoLTE calls**

The Wireshark above shows that after several IPSec (ESP) packets, S-CSCF is sending a SIP INVITE for UE 03 to UE 04. To be more precise,
```
Request-Line: INVITE sip:0398765432100;phone-context=0498765432100@0498765432100;user=phone SIP/2.0
...
Record-Route URI: sip:mo@10.4.128.21:6101;lr=on;ftag=7b3fae13;rm=8;did=078.654
```
The SIP port of the caller (`contact`) will also be passed to the callee,
```
Contact URI: sip:0498765432100@192.168.101.3:6400;alias=192.168.101.3~6401~1
```
After S-CSCF forwarded the INVITE to P-CSCF, it returns a 100 Trying, and contacts with the callee via IPSec:

This can be contrasted when the callee does not support IPSec. After 100
Trying, a UE that does not support IPSec is sent a SIP INVITE in clear text:

#### 9. Known issues
- IPv6 is not supported.
#### 10. References
- [https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284](https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284)
- [https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/](https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/)
- [https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html)
 If CoIMS is used to force enable VoLTE on the Android device, it should look like in the screenshot below:
If CoIMS is used to force enable VoLTE on the Android device, it should look like in the screenshot below:
 **Networking issues**
PCAP files of successful calls can be found on [VoLTE Setup](https://open5gs.org/open5gs/docs/tutorial/02-VoLTE-setup/).
When DNS is not properly set, you may end up with 478 Unresolvable destination (478/SL):

If the port if not open, or DNS is not properly configured, the phone cannot reach P-CSCF and fails.

If there is an NAT between PGW and P-CSCF, IPsec-NAT would not work, and the PCAP looks like the one below. Note that you need to run P-CSCF as root, in
order to add xfrm state and policy.

#### 8. Successful calls
Herle Supreeth has shared PCAP files of successful calls, including
- [IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to Non-IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_nonipsec_call.pcapng)
**UE registration**

From the screenshot, we see a UE that supports IPSec got a response from S-CSCF, indicating that ipsec-3gpp is supported, protocol is ESP (ethernet proto 50, IPSec). Client port (port-c) is 5100 and server port (port-s) 6100.
Refer to [IMS/SIP - Basic Procedures](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/IMS_SIP_Procedure_Reg_Auth_IPSec.html) if you want to know more.
Also, notice that packets after 401 Unauthorized are transmitted over ESP.
If a UE does not support IPSec, you don't see the "security-server", as shown below:

**VoLTE calls**

The Wireshark above shows that after several IPSec (ESP) packets, S-CSCF is sending a SIP INVITE for UE 03 to UE 04. To be more precise,
```
Request-Line: INVITE sip:0398765432100;phone-context=0498765432100@0498765432100;user=phone SIP/2.0
...
Record-Route URI: sip:mo@10.4.128.21:6101;lr=on;ftag=7b3fae13;rm=8;did=078.654
```
The SIP port of the caller (`contact`) will also be passed to the callee,
```
Contact URI: sip:0498765432100@192.168.101.3:6400;alias=192.168.101.3~6401~1
```
After S-CSCF forwarded the INVITE to P-CSCF, it returns a 100 Trying, and contacts with the callee via IPSec:

This can be contrasted when the callee does not support IPSec. After 100
Trying, a UE that does not support IPSec is sent a SIP INVITE in clear text:

#### 9. Known issues
- IPv6 is not supported.
#### 10. References
- [https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284](https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284)
- [https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/](https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/)
- [https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html)
**Networking issues**
PCAP files of successful calls can be found on [VoLTE Setup](https://open5gs.org/open5gs/docs/tutorial/02-VoLTE-setup/).
When DNS is not properly set, you may end up with 478 Unresolvable destination (478/SL):

If the port if not open, or DNS is not properly configured, the phone cannot reach P-CSCF and fails.

If there is an NAT between PGW and P-CSCF, IPsec-NAT would not work, and the PCAP looks like the one below. Note that you need to run P-CSCF as root, in
order to add xfrm state and policy.

#### 8. Successful calls
Herle Supreeth has shared PCAP files of successful calls, including
- [IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE registration for VoLTE]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_reg.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [Non-IPSec UE to IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/nonipsec_to_ipsec_call.pcapng)
- [IPSec UE to Non-IPSec UE calling]({{ site.url }}{{ site.baseurl }}/assets/pcapng/ipsec_to_nonipsec_call.pcapng)
**UE registration**

From the screenshot, we see a UE that supports IPSec got a response from S-CSCF, indicating that ipsec-3gpp is supported, protocol is ESP (ethernet proto 50, IPSec). Client port (port-c) is 5100 and server port (port-s) 6100.
Refer to [IMS/SIP - Basic Procedures](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/IMS_SIP_Procedure_Reg_Auth_IPSec.html) if you want to know more.
Also, notice that packets after 401 Unauthorized are transmitted over ESP.
If a UE does not support IPSec, you don't see the "security-server", as shown below:

**VoLTE calls**

The Wireshark above shows that after several IPSec (ESP) packets, S-CSCF is sending a SIP INVITE for UE 03 to UE 04. To be more precise,
```
Request-Line: INVITE sip:0398765432100;phone-context=0498765432100@0498765432100;user=phone SIP/2.0
...
Record-Route URI: sip:mo@10.4.128.21:6101;lr=on;ftag=7b3fae13;rm=8;did=078.654
```
The SIP port of the caller (`contact`) will also be passed to the callee,
```
Contact URI: sip:0498765432100@192.168.101.3:6400;alias=192.168.101.3~6401~1
```
After S-CSCF forwarded the INVITE to P-CSCF, it returns a 100 Trying, and contacts with the callee via IPSec:

This can be contrasted when the callee does not support IPSec. After 100
Trying, a UE that does not support IPSec is sent a SIP INVITE in clear text:

#### 9. Known issues
- IPv6 is not supported.
#### 10. References
- [https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284](https://github.com/onmyway133/blog/issues/284)
- [https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/](https://realtimecommunication.wordpress.com/2015/05/26/at-your-service/)
- [https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html](https://www.sharetechnote.com/html/Handbook_LTE_VoLTE.html)